User Presence Status in Microsoft Teams
There are many different user presence states in Microsoft Teams. In some cases, users can select their status by themselves, while other states are displayed automatically.
But what does each Microsoft Teams presence status mean? How are they selected, and by whom?
Here we share with you everything you need to know about your Microsoft Teams presence.
Like this infographic? Share it with your network!
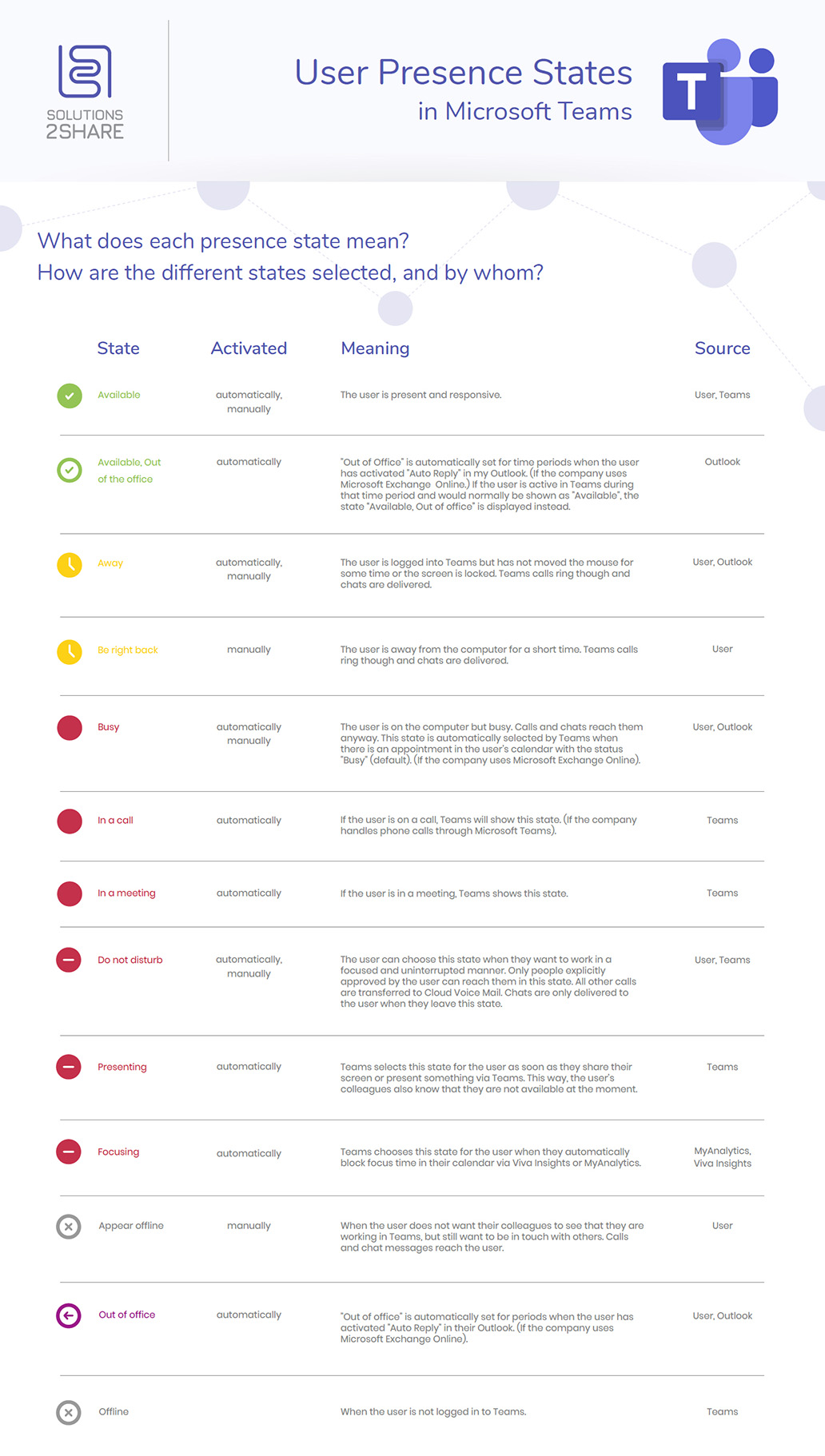
These are the different Teams User Presence Status:
The status “Available” is activated either automatically or manually. The user is present and responsive.
The status “Available, out of office” is only activated automatically. “Out of Office” is automatically set for time periods when the user has activated “Auto Reply” in Outlook. (If the company uses Microsoft Exchange Online.) If the user is active in Teams during that time period and would normally be shown as “Available”, the Microsoft Teams status “Available, Out of office” is displayed instead.
The status “Away” is activated either automatically or manually. The user is logged into Teams but has not moved the mouse for some time or the screen is locked. Teams calls ring though and chats are delivered.
The status “Be right back” can only be activated manually. The user is away from the computer for a short time. Teams calls ring though and chats are delivered.
The status “Busy” is activated either automatically or manually. The user is on the computer but busy. Calls and chats reach them anyway. This Teams status is automatically selected by Teams when there is an appointment in the user’s calendar with the status “Busy” (default). (If the company uses Microsoft Exchange Online).
The status “In a call” is only activated automatically. If the user is on a call, Teams will show this state. (If the company handles phone calls through Microsoft Teams).
The status “In a meeting” is only activated automatically. If the user is in a meeting, this MS Teams status is displayed.
The status “Do not disturb” is activated either automatically or manually. The user can choose this status when they want to work in a focused and uninterrupted manner. Only people explicitly approved by the user can reach them in this status. All other calls are transferred to Cloud Voice Mail. Chats are only delivered to the user when they leave this Teams status.
The status “Presenting” is only activated automatically. Teams selects this user status as soon as they share their screen or present something via Teams. This way, the user’s colleagues also know that they are not available at the moment when the Teams presenting status is shown.
The status “Focusing” is only activated automatically. Teams chooses this state for the user when they block focus time in their calendar via Viva Insights or MyAnalytics.
The status “Appear offline” can only be activated manually. When the user does not want their colleagues to see that they are working in Teams, but still want to be in touch with others. Calls and chat messages reach the user.
The status “Out of office” is only activated automatically. “Out of office” is automatically set for periods when the user has activated “Auto Reply” in their Outlook. (If the company uses Microsoft Exchange Online).
The status “Offline” is only activated automatically when the user is not logged in to Teams.
With this overview, you will now be able to understand your Microsoft Teams presence status.
With Teams Manager you can easily keep control of your Microsoft Teams. Get started with Teams governance today and book a free demo with your personal Teams specialist.

There are always questions and challenges when you want to keep control of your Microsoft Teams. Is there anything else you would like to know? Let us know in the comments below!

Head of Marketing & Sales at Solutions2Share – Florian Pflanz has 6 years of M365 experience and has been involved in numerous projects concerning Microsoft Teams governance. In over 200 workshops, he has collected extensive knowledge and best practices regarding Microsoft Teams and companies’ management requirements.



